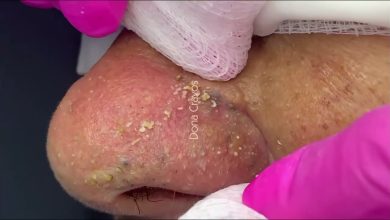
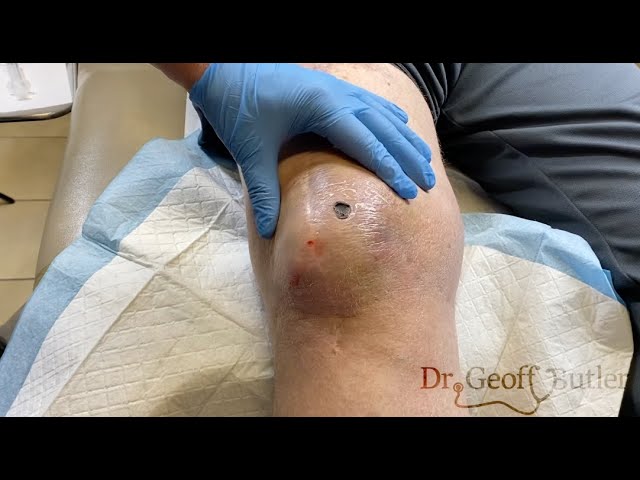
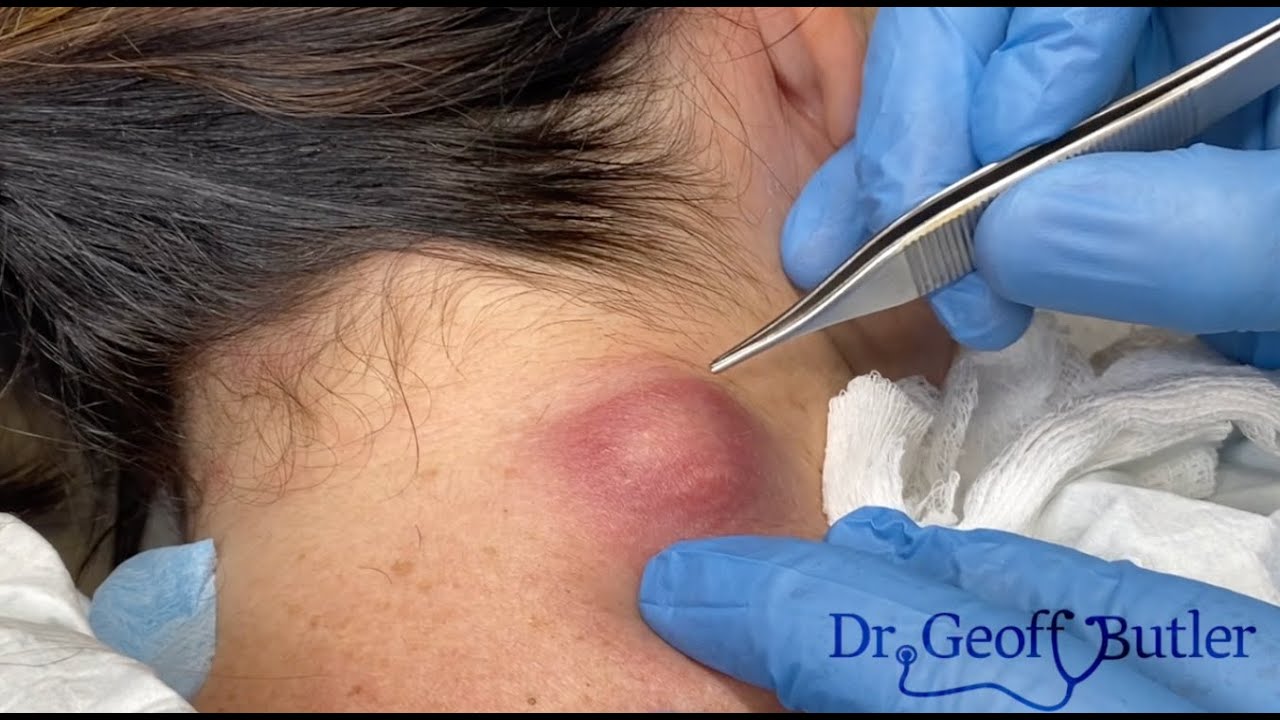
Drainage of an Infected Cyst in Front of the Ear: Causes, Treatment, and Care Tips
Cysts are common skin conditions that can occur in various parts of the body, and when located near the ear, they can become particularly uncomfortable. An infected cyst in front of the ear can cause pain, swelling, and irritation, making it essential to understand its causes, treatment options, and how to care for it properly. This article will delve into what an infected cyst is, why it occurs, the drainage procedure, and tips on managing the condition to ensure proper healing.
What is a Cyst?
A cyst is a sac-like structure that can form on the skin or inside the body. It is usually filled with fluid, air, or other materials. Cysts in front of the ear are often sebaceous cysts, which are non-cancerous lumps that form in the sebaceous glands (oil-producing glands in the skin). They can develop due to blocked ducts, excessive oil production, or trauma to the skin.
Causes of an Infected Cyst in Front of the Ear
While cysts are typically harmless, they can become infected for several reasons. Here are some common causes of an infected cyst:
- Blocked Pores or Hair Follicles: When the pore or hair follicle becomes blocked, oils and dead skin cells can accumulate inside, leading to cyst formation. If bacteria enter the cyst, it can cause infection.
- Trauma to the Area: Scratching, squeezing, or any injury to the cyst can introduce bacteria, leading to an infection. This is why it’s important to avoid touching or manipulating cysts unnecessarily.
- Poor Hygiene: Lack of proper cleaning around the area can lead to the accumulation of dirt and oils, which can increase the risk of infection.
- Underlying Skin Conditions: Conditions such as acne, eczema, or other dermatological issues can make individuals more susceptible to developing cysts that may become infected.
- Weakened Immune System: People with compromised immune systems are more prone to infections, which can make cysts more likely to become infected.
Signs and Symptoms of an Infected Cyst
An infected cyst near the ear will show several telltale signs, including:
- Redness and Swelling: The cyst becomes visibly swollen, and the skin around it may appear red or inflamed.
- Pain and Tenderness: The infected area will be sore to the touch, and pain may worsen with pressure or movement.
- Pus or Fluid Drainage: An infected cyst may start to leak pus, which can be thick and yellowish in color.
- Warmth: The skin around the cyst may feel warm to the touch due to inflammation and infection.
- Fever: In rare cases, the infection can lead to systemic symptoms such as fever.
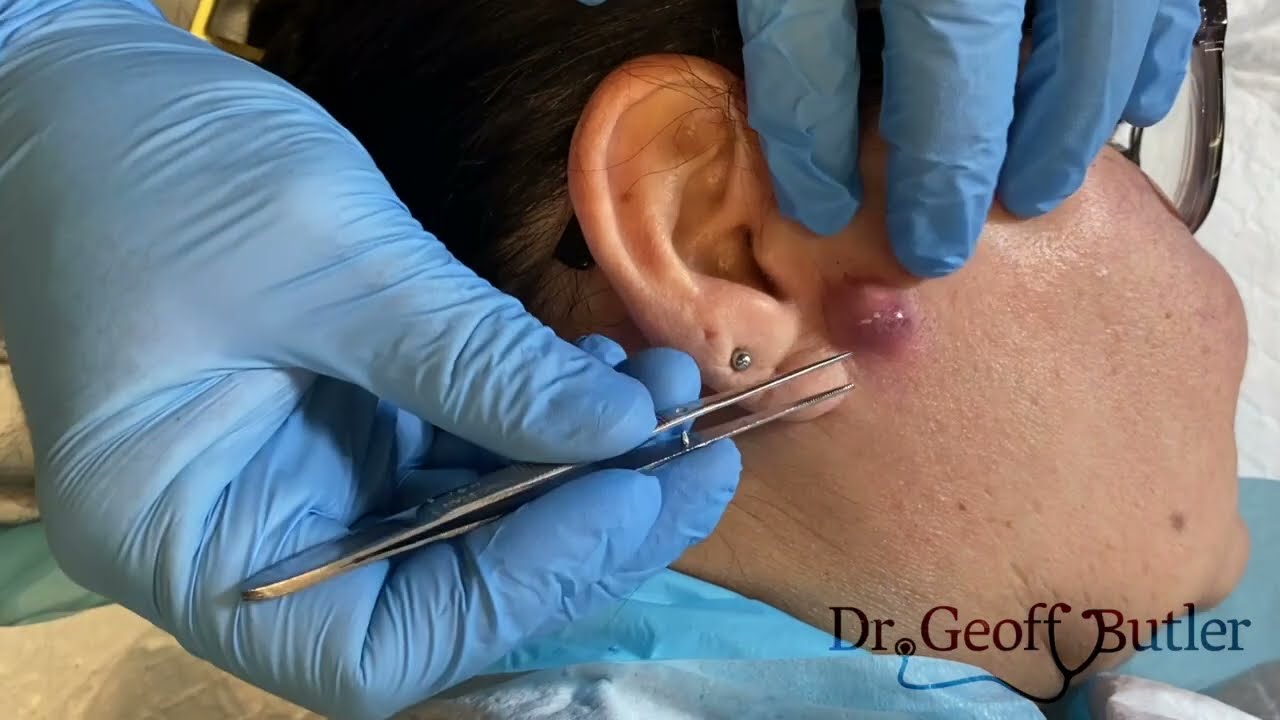
Drainage of an Infected Cyst: Treatment Options
If you suspect an infected cyst in front of the ear, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. While some cysts can resolve on their own, infected cysts require treatment to prevent further complications.
1. At-Home Care (for mild cases)
If the cyst is not severely infected, you may be able to manage it at home with these simple steps:
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the cyst for 10-15 minutes a few times a day can help soften the cyst, reduce swelling, and encourage drainage.
- Keep the Area Clean: Gently wash the affected area with mild soap and water to avoid further irritation.
- Avoid Squeezing: Never attempt to squeeze or pop the cyst, as it can worsen the infection and spread bacteria.
2. Medical Drainage (for moderate to severe cases)
For infected cysts that do not improve with at-home care or are causing significant discomfort, medical intervention is necessary. The drainage procedure is typically performed by a healthcare provider under sterile conditions. Here’s what you can expect:
- Incision: The doctor may make a small incision in the cyst to allow the pus or fluid to drain out. This is often done under local anesthesia to minimize pain.
- Sterilization: After draining, the cyst cavity will be cleaned and sterilized to prevent the infection from spreading.
- Dressing: A bandage or dressing may be applied to keep the area clean and protect it from further infection.
3. Antibiotics
If the cyst infection is severe, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics to help fight the infection and reduce inflammation. Antibiotics are typically given if there is concern that the infection might spread or worsen.
4. Surgical Removal
In some cases, when cysts are recurrent or particularly troublesome, the doctor may recommend surgical removal. This procedure involves excising the entire cyst, including the sac, to prevent future cyst formation.
Aftercare Tips for Managing an Infected Cyst
Once the cyst has been drained, proper aftercare is essential to ensure healing and avoid complications:
- Follow Post-Drainage Instructions: If your healthcare provider performed a drainage procedure, follow their advice on wound care. This may include keeping the area clean, applying topical antibiotics, and changing the dressing regularly.
- Avoid Touching the Area: To minimize the risk of further infection, avoid touching, rubbing, or scratching the cyst area.
- Monitor for Complications: Keep an eye on the cyst for any signs of recurrent infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus production. Seek medical attention if these symptoms persist.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash the affected area gently with mild soap and water, and avoid using harsh chemicals or scrubbing the cyst, as this can irritate the skin and delay healing.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you notice any of the following, it’s crucial to contact your healthcare provider immediately:
- Rapid Growth of the Cyst: If the cyst grows quickly or becomes significantly larger.
- Severe Pain: Intense pain that is not relieved with over-the-counter pain medications.
- Fever: The development of a fever could indicate a spreading infection.
- Recurrent Cysts: If cysts continue to form in the same area, it may be necessary for your doctor to explore other treatments.
Conclusion
An infected cyst in front of the ear can be a frustrating and painful condition, but with proper treatment, it can be effectively managed. Whether through at-home care or medical intervention, draining the cyst and following aftercare guidelines are essential steps in ensuring complete healing. Remember, never attempt to pop or squeeze an infected cyst yourself, as this can lead to more severe complications. If in doubt, always seek the advice of a healthcare professional to get the most appropriate care.
By understanding the causes, treatment options, and aftercare, you can take the necessary steps to address an infected cyst and prevent future occurrences.